Environmental Pollution:叶面喷施巯基化合物DMSA抑制稻米中重金属镉铅砷的积累
作者: 来源: 2021-08-27

农业农村部环境保护科研监测所重金属生态毒理创新团队发现,叶面喷施巯基化合物2,3-二巯基丁二酸(DMSA)能够抑制水稻旗叶中重金属的迁移,进而降低籽粒中镉、铅、砷的积累,在不影响稻米营养元素含量的同时,缓解水稻重金属复合污染。相关成果发表于Environmental Pollution(IF= 8.071)。
论文通讯作者为黄永春副研究员,研究工作得到国家自然科学基金、中国农科院协同创新项目和国家重点研发计划项目的资助。
Highlights
•Spraying DMSA simultaneously decreases the contents of Cd, As and Pb in brown rice.
•DMSA has no significant effect on the contents of nutrient elements in brown rice.
•Spraying DMSA promotes the immobilization of Cd, As and Pb in rice flag leaves.
Abstract
Mixed pollution due to heavy metals (HMs), especially cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and arsenic (As), seriously endangers the safety of food produced in paddy soil. In the field experiments, foliar application of 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) at the flowering stage was found to significantly reduce the levels of Cd, Pb, total As, and inorganic As (iAs) in rice grains by 47.95%, 61.76%, 36.37%, and 51.24%, respectively, without affecting the concentration of metallonutrients, including Mn, K, Mg, Ca, Fe, and Zn. DMSA treatment significantly reduced the concentrations of Cd, Pb, and As in the panicle node, panicle neck, and rachis, while those in the flag leaves were significantly increased by up to 20.87%, 49.40%, and 32.67%, respectively. DMSA application promoted the transport of HM from roots and lower stalks to flag leaves with a maximum increase of 34.55%, 52.65%, and 46.94%, respectively, whereas inhibited the transport of HM from flag leaves to panicle, rachis, and grains. Therefore, foliar application of DMSA reduced Cd, Pb, and As accumulation in rice grains by immobilizing HMs in flag leaves. Thus, this strategy could act as a promising agronomic measure for the remediation of mixed HM contamination in paddy fields.
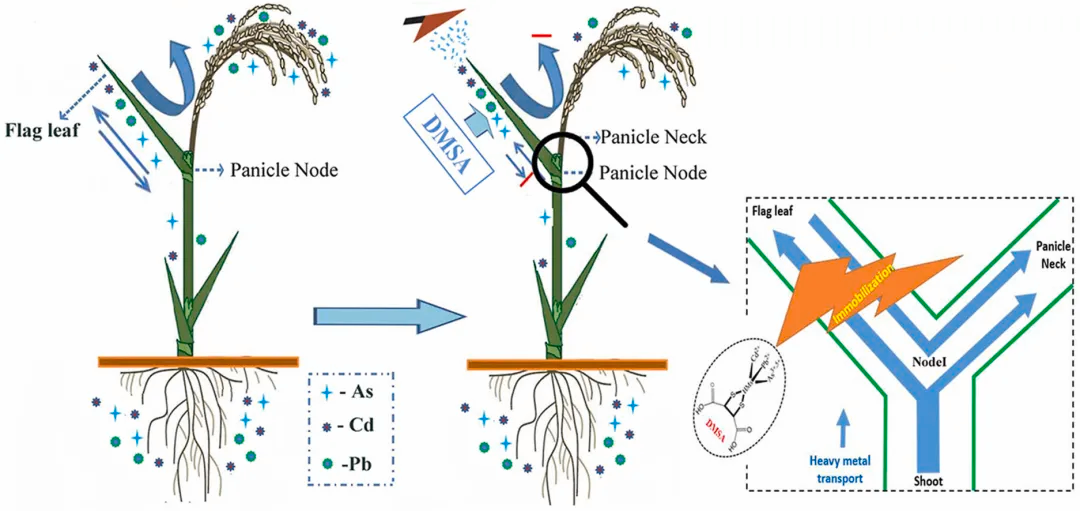
稻田土壤中镉(Cd)、铅(Pb)、砷(As)等重金属的复合污染严重威胁粮食安全生产。田间实验发现,在水稻开花期叶面喷施2,3-二巯基丁二酸(DMSA),能够显著降低籽粒中Cd、Pb、总As和无机砷(iAs)的含量,降幅分别达47.95%、61.76%、36.37%和51.24%,同时不影响其他金属营养元素Mn、K、Mg、Ca、Fe和Zn的含量。深入研究发现,叶面喷施DMSA显著降低了水稻穗节、穗颈和穗轴中Cd、Pb和As含量,与之相反,旗叶中Cd、Pb和As的含量却显著提高了20.87%、49.40%和32.67%。也就是说,DMSA处理抑制了重金属从旗叶向穗轴和籽粒的转运。同时,叶面喷施DMSA提高了重金属Cd、Pb和As从水稻根和茎向旗叶的转运系数,最大增幅分别达34.55%、52.65%和46.94%。由此可见,叶面施用DMSA可通过将重金属固定在水稻旗叶中,降低Cd、Pb和As在水稻籽粒中的积累。因此,叶面喷施DMSA作为修复稻田重金属复合污染的一种农艺措施,具有很好的应用前景。













